Entrepreneurial Process: Meaning, Overview & Stages – Embarking on the journey of entrepreneurship is like setting sail on uncharted waters. Understanding the entrepreneurial process is akin to having a reliable compass in hand. The intricacies of this venture creation process have become a focal point in the realm of current entrepreneurship. where budding entrepreneurs are on the cusp of turning their ideas into reality. This process is a fascinating terrain to explore, let’s see why it is.
What is the Entrepreneurial Process
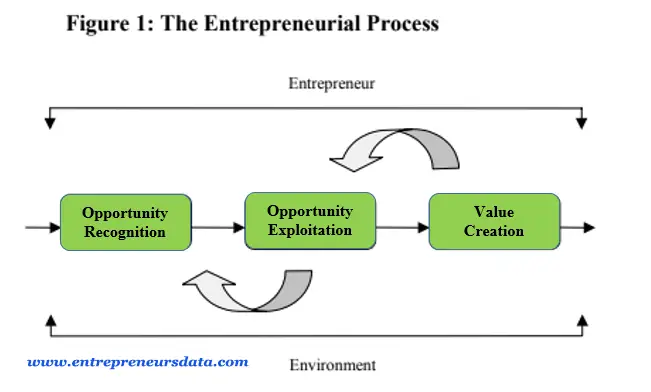
The entrepreneurial process is the sequence of steps and activities involved in starting and managing a new venture. It encompasses the identification of opportunities, gathering resources, creating a business plan, launching the venture, and managing its growth and development.
The entrepreneurial process is a thrilling journey filled with opportunities and challenges. It’s about spotting a chance, seizing it with a solid plan, and then creating value that keeps customers coming back for more. It’s where ideas take flight and become thriving ventures that make a difference in the market.
Learn more about Corporate Entrepreneurship – Click here
Stages of the Entrepreneurial Process
We label the first level of the technique opportunity recognition. The invention and assessment of opportunities are part of this technique. Inside the possibility reputation system, initial ideas evolve into fully-fledged enterprise opportunities.
Inside the second stage, ‘opportunity exploitation’, important sources are combined to enable exchange with the market. The acknowledged commercial enterprise opportunity is translated into an actual resource.
When the imparting is taken up with the aid of the market inside the third stage. The possibility of exploitation ended with the advent of value. We use the expression value creation in place of wealth creation to stress the feasible non-economic outcomes of the entrepreneurial process. The advent of cost seems because of the final result of the entrepreneurial system. The process seems to be linear and sequential, whereas, in reality, it is dynamic and iterative.
Let’s discuss the stages of the entrepreneurial process one by one.
01. Opportunity Recognition in Entrepreneurial Process
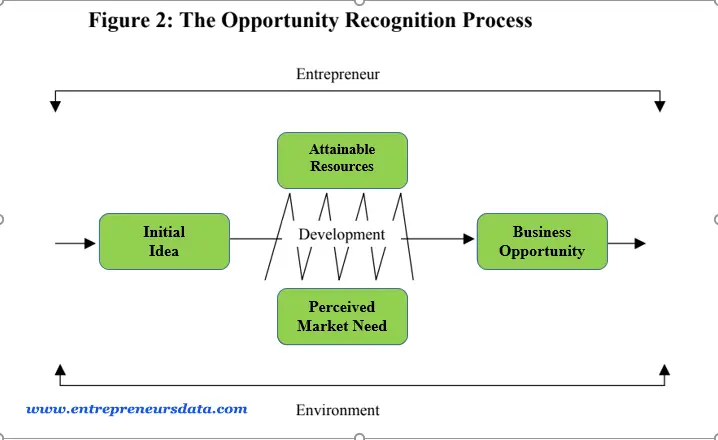
The process of opportunity recognition begins with an initial idea, which can come from employment, hobbies, social encounters, or observation. Entrepreneurs often seek opportunities for dissatisfaction and are subconsciously motivated by their talents, environmental context, and societal values. A preliminary idea is crucial for the entrepreneurial process, which involves full-scale development, and social, cultural, and personal elements.
The idea is evaluated and refined until it becomes a complete business opportunity. The process is evolutionary and iterative, involving cognitive sports, data accumulation, and idea introduction. The goal is to overcome expected challenges and maximize potential advantages.
- Information Scanning
- Thinking through Talking
- Information Seeking
- Assessing Resources
Through these activities, the preliminary concept is evolved and evaluated into a complete-fledged commercial enterprise opportunity. The evaluation of possibilities, in the course of the filtration or screening system, is a vital step inside the system of growing preliminary ideas into commercial enterprise opportunities.
The new breed of entrepreneurship – Click here
The Role of The Entrepreneur in the Opportunity Recognition Process
Entrepreneurship is a crucial factor in recognizing opportunities. Historically, the reason for entrepreneurship was attributed to psychological development. Mental studies can be divided into two groups: identifying entrepreneurial personality traits and examining socio-mental or socio-cultural factors. Socio-cultural attributes, such as ethnicity, gender, and family background, can influence entrepreneurial behavior. Existence-direction changes, such as job loss or cultural influences, can lead to business formation.
However, the effect of personality on entrepreneurial behavior remains inconclusive. Recent research has focused on differences in understanding, statistics, and cognitive behavior, highlighting the importance of prior knowledge and experience in entrepreneurship. Entrepreneurial alertness is also important, as entrepreneurs today interpret statistics differently than executives.
Businessman vs entrepreneur – Click here
The Role of The Environment in the Opportunity Recognition Process
The environment significantly influences the opportunity recognition process, with social contexts playing a crucial role in determining the success of entrepreneurial opportunities. Marketers use their networks to gather information. They gather statistics and access resources and information. To increase their possibilities, entrepreneurs interact with the community. Socioeconomic, cultural, technical, and political issues all have an impact on their success. Technological advancements and favorable political conditions can also stimulate entrepreneurs to start businesses.
02. Opportunity Exploitation in Entrepreneurial Process
Opportunity exploitation is a crucial phase in the entrepreneurial process, involving the transition from idea to concrete business concept, the quest for control, commitment to exploitation, modes of exploitation, factors influencing the decision, resource gathering and integration, and the role of networking. Entrepreneurs must identify specific resource requirements and find potential providers, then engage in strategic maneuvers to obtain these resources. Social networking plays a pivotal role in this process, as entrepreneurs act as organizers and coordinators of resources.
Opportunity exploitation is the bridge between ideation and market success, involving resource gathering, strategic networking, and the transformation of ideas into real-world solutions. The choices made during this phase can determine whether a new business is born or an existing one evolves to seize a fresh opportunity. It’s the heart of entrepreneurship, where ideas become action, and innovation meets the marketplace.
The Role of The Entrepreneur in the Opportunity Exploitation Process
Opportunity exploitation in entrepreneurship involves turning potential into tangible products or services. The entrepreneur’s mental attributes, such as risk aversion and prior experience, are crucial in recognizing and exploiting opportunities. Knowledge and experience are key, as they provide insights and expertise needed to make ventures a reality.
Successful entrepreneurs are action-oriented, taking action to turn their ideas into tangible businesses. Information processing styles also play a role in entrepreneurship, with creative individuals better equipped to build a resource base. For example, Alice, a risk-taker with experience in the sustainability industry, sees an opportunity in the growing demand for eco-friendly products. Her creative thinking helps her find unique ways to build her resource base.
The Role of The Environment in the Opportunity Exploitation Process
In the dynamic world of entrepreneurship, the environment in which an entrepreneur operates plays a dual role in the opportunity exploitation process. An entrepreneur’s network is a valuable resource, providing access to financial capital, emotional support, valuable information, and advice. The competitive landscape also plays a crucial role in entrepreneurship, with a favorable environment and high demand enabling entrepreneurs to exploit opportunities. Timing matters also play a role, with the age of technology and the competitive landscape influencing opportunity exploitation.
In industries with infancy, innovation is abundant, and lower competition and opportunity costs can be game-changers. For example, Sarah, an entrepreneur with a passion for sustainable fashion, can leverage her network to access investors and gain valuable insights into the eco-friendly textile market. This combination of resources and timing provides a strong foundation for success in the market.
Model of the opportunity exploitation process
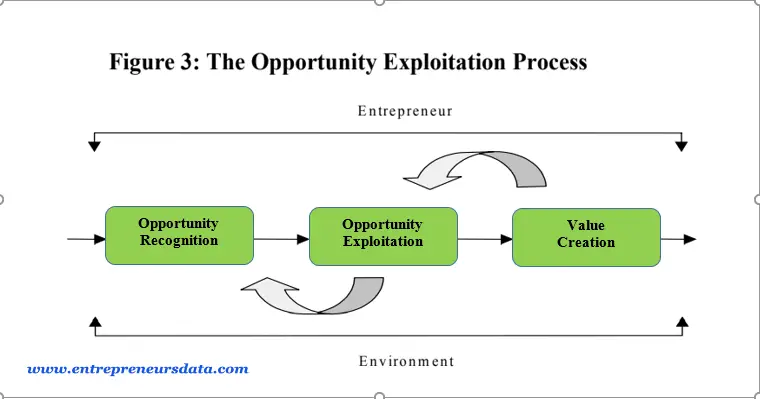
The “opportunity exploitation process” is a crucial phase in the entrepreneurial journey, involving the transformation of a promising business opportunity into a practical business concept. This process includes translating the idea into a complete package, including resources, organizational structure, products or services, and a marketing plan. The entrepreneur plays a pivotal role in driving this transformation. They shape the business concept and set it on the path to success. The environment also plays a significant role, in providing support, resources, and competition. Entrepreneurs must be flexible and pivoting in times of challenges.
03. Value Creation in Entrepreneurial Process
Value creation is a crucial aspect of the entrepreneurial process, as it drives the journey, motivates everyone involved, and serves as a catalyst for future entrepreneurship. The perceived value created through opportunity exploitation motivates entrepreneurs customers, and even potential investors.
The outcomes of the entrepreneurial process can shape the future, as lessons learned and experiences gained to contribute to the development of human and intellectual capital. Even failures can be valuable lessons, leading to new insights, strategies, and innovative ideas. Therefore, value creation is not just about the present but also a driving force in shaping the future of entrepreneurship.
Did you know the “Difference between Businessman and Entrepreneur” – Click here
Levels and Types of Value Creation
Value creation in the realm of entrepreneurship isn’t a one-dimensional concept; it operates on multiple levels and takes various forms. Entrepreneurship impacts both personal and societal levels, with entrepreneurs seeking to accumulate wealth for personal success. This can stimulate economic growth, create new markets, and generate employment, contributing to society’s betterment. However, not all forms of wealth creation lead to societal benefits, such as organized crime or rent-seeking.
Entrepreneurial activities can also trigger changes within specific industries and regional economies. Different forms of value emerge. Including economic, non-economic, positive, negative, immediate, or long-term. Entrepreneurial opportunities can have a spectrum of outcomes, from success to failure.
The Role of The Entrepreneur in the Value Creation Process
The role of the entrepreneur in the value-creation process is a complex interplay of various factors. Let’s dissect this intricate relationship.
1. Ambiguous Impact of Personality
Studies on the direct influence of an entrepreneur’s personality on value creation have shown contradictory findings. Although personality qualities are undoubtedly important, the relationship is not simple. The entrepreneur’s personality can influence value creation, but this influence is often mediated by user behavior and external factors.
2. The Mediating Factors
An entrepreneur’s abilities and personality traits, such as creativity and strategic thinking, indirectly affect value creation. This influence is channeled through their work approach and focus. High-performing entrepreneurs, those driving successful firms, tend to concentrate on strategic tasks that drive sales growth, rather than getting bogged down in operational details.
3. The Critical Evaluation
At a certain juncture, the entrepreneur must evaluate the progress of opportunity exploitation. This involves weighing the expected payoffs against the results achieved. Based on this evaluation, the entrepreneur may decide to continue, pivot, or even abandon the venture. The decision to exit or continue is deeply linked to the company’s financial performance and a predefined performance threshold.
4. Exit Strategies
In the entrepreneurial world, exits are not uncommon. Even when a venture is performing well, entrepreneurs may decide to exit the stage. They might opt to sell the business. Also, aiming to capitalize on its value, as was seen during the dot-com boom. Different exit strategies, such as Initial Public Offerings or mergers and acquisitions, are often considered.
5. Succession and Organizational Mortality
However, the exit of the founding entrepreneur, especially in a relatively young company, can pose a significant challenge. It may lead to a succession problem, potentially threatening the organization’s survival. This challenge can result in organizational mortality, where the company struggles to find suitable leadership to carry it forward.
Corporate entrepreneurship – Click here
Conclusion
This exploration of the entrepreneurial process delves into its fundamental elements, from idea initiation to thriving venture creation. Successful entrepreneurship is a dynamic interplay between an entrepreneur’s unique characteristics and the environment. It’s an art and science, blending individual ingenuity and environmental dynamics. Understanding this journey helps entrepreneurs navigate challenges, seize opportunities, and shape the future of business and society.
FAQs on Entrepreneurial Process
What is the entrepreneurial process?
The entrepreneurial process is the series of steps and activities involved in starting and managing a new business. It includes opportunity identification and resource acquisition. Also, business plan creation, venture launch, and growth and development management.
Why entrepreneurship is a process?
Entrepreneurship is a process because it is not a single event. It is a journey that requires continuous learning. Also, adaptation, and growth. Entrepreneurs must be able to identify opportunities and develop products or services. Then they can meet those opportunities, and then successfully launch and manage their enterprises. The entrepreneurial process is complicated and challenging. It is also one that can be very rewarding.
What are the four (4) aspects of the entrepreneurial process?
The entrepreneurial process has four aspects.
- The capacity to spot market issues or unmet wants that a new good or service may solve is known as opportunity identification.
- The capacity to create and carry out a strategy to take advantage of a chance that has been recognized is known as opportunity exploitation.
- Value creation is the process of creating and delivering goods or services that buyers are prepared to pay for.
- The capacity to get the resources required to launch and run a firm, including cash, personnel, and tools, is known as resource acquisition.
What are the three (3) major parts of the entrepreneurial process?
The three major parts of the entrepreneurial process are:
A. Opportunity Recognition
Entrepreneurial traits and experiences influence identifying untapped market needs, while the entrepreneurial ecosystem provides necessary support, resources, and networks for successful opportunity recognition.
B. Opportunity Exploitation
Opportunity exploitation involves entrepreneurs identifying and utilizing identified opportunities, leveraging resources, and leveraging the environment to access capital, markets, and support. This process involves a step-by-step journey from idea inception to product creation.
C. Value Creation
The value-creation process involves entrepreneurs shaping products and services to cater to customer needs, transforming societal levels from personal wealth to broader economic impact.
What are the six steps in the entrepreneurial process
The six steps in the entrepreneurial process are
- Idea generation – It is the process of coming up with novel business ideas.
- Opportunity evaluation – This is the process of considering the viability of business ideas.
- Business planning – This is the process of developing a roadmap for how the firm will be launched and operated.
- Resource acquisition – This is the process of collecting the resources required to start and operate the business.
- Venture launch – This is the process of getting the business to market.
- Growth management – This is the procedure of growing and extending the business.