Types of Corporate Entrepreneurship: -In the 21st Century, corporate entrepreneurship has increasingly been identified as one of the best ways to achieve high grades in organizational performance. In this article, we are discussing,
Corporate Entrepreneurship Meaning
Corporate entrepreneurship meaning: – Corporate entrepreneurship meaning is the development of new businesses within established firms. To be accurate, it covers all incumbent-firm activities that aim at improving the organization. It includes administrative structures to improve its creative ability and pave the path for new businesses to exist in the long run.
Businesses cannot secure if they are not prepared to put their gains back into play, dominate new markets, develop the latest technologies, and create novel business models. We can say corporate entrepreneurship is an umbrella term for all entrepreneurial actions which can create competitive advantages.
According to the resource-based theory, corporate entrepreneurship is a vital indicator and a critical measure for transforming resources into competitive goals. Corporate entrepreneurship produces product innovations, administrative innovations, techniques, and methods of thinking for organizations to revitalize and redefine both their structure and their associated markets.
Corporate entrepreneurship is crucially significant to the survival, profitability, and development of an organization. This is because corporate entrepreneurship actions manage to foster creativity and innovation as well as inspire a culture of calculated risk-taking throughout organizational processes. This may reinforce the company’s standing in existing markets by entering new and lucrative growth fields.
More definitions for CE – Click here
Types of Corporate Entrepreneurship
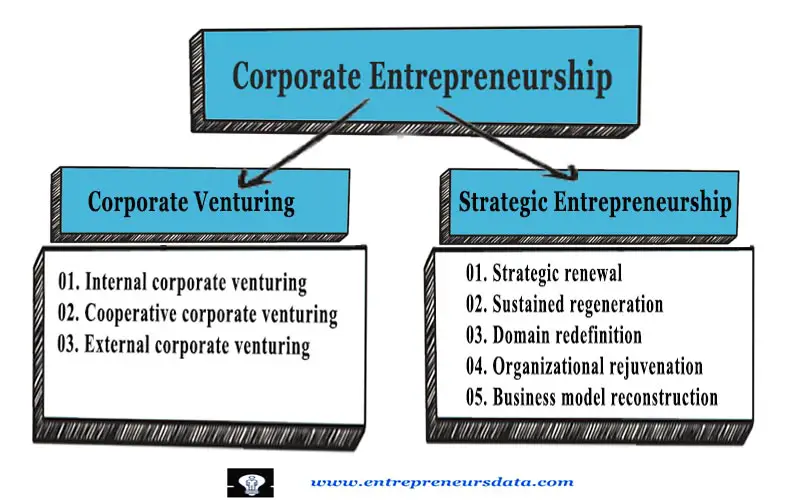
Corporate entrepreneurship types contain two major parts. Those are;
- Corporate Venturing – New venture creation within current organizations
- Strategic Entrepreneurship – Transformation of current organizations via strategic renewal
Corporate venturing approaches have as their commonality the acquisition of new businesses (or parts of new businesses through equity investments) to the corporation. This can be executed through three implementation ways
- Internal Corporate Venturing
- Cooperative Corporate Venturing
- External Corporate Venturing
Strategic entrepreneurship approaches have as their commonality the exhibition of large-scale or otherwise highly significant innovations that are assumed in the firm’s goal of competitive advantage. These creations may or may not result in new businesses for the corporation. In the strategic entrepreneurship approach, we can identify five innovation areas. These are – the firm’s strategy, product offerings, served markets, internal organization (ex., structure, processes, and capabilities), or business model.
Youth Entrepreneurship – Click here
Corporate Venturing in Corporate Entrepreneurship

Corporate venturing is the first main category of corporate entrepreneurship and it contains different methods for creating, adding to, or investing in novel businesses.
Types of Corporate Venturing
This comprises three major types of corporate venturing. Those types are,
Internal Corporate Venturing
With internal corporate venturing, novel businesses are constructed and owned by the company. These businesses generally reside within the corporate network but, sometimes, may be located outside the firm and function as semi-autonomous entities. Among internal corporate ventures that reside within the firm’s administrative borders, some may be created and exist as part of a pre-existing internal organization structure and others may be housed in newly formed organizational entities within the corporate system.
There are two groups of motives that push the practice of internal corporate venturing. Those are:
- Leveraging – to use current corporate competencies in new product or market arenas;
- Learning – to develop new knowledge and skills that may be valuable in current products or market arenas.
Youth Entrepreneurs Characteristics – Click here
Cooperative Corporate Venturing
Cooperative corporate venturing (joint corporate venturing, collaborative corporate venturing) refers to entrepreneurial action in which new businesses are created and owned by the corporation together with one or more external development associates. Cooperative ventures generally exist as external entities that function beyond the organizational borders of the founding partners.
External Corporate Venturing
External corporate venturing refers to entrepreneurial action in which new businesses are formed by parties outside the corporation and subsequently invested in (through the assumption of equity positions) or acquired by the corporation. These external businesses are normally very young ventures which are in the early growth stage of a firm.
In practice, new businesses might be created through a single venturing mode, any two venturing modes, or all three venturing modes. A firm’s entire venturing activity is equivalent to the sum of the ventures enacted through the internal, cooperative, and external modes. With corporate venturing, developing an entirely new business is the primary objective. It is impossible, however, to assess the success or failure of corporate venturing initiatives unless it is clear what administration goals were in the foremost place. Organizations must build venture evaluation and control procedures that evaluate venture performance on standards that follow the venture’s founding motive.
Specific Reasons for Corporate Venturing
- To use under-utilized resources – building a new business by using internal capabilities that remain inactive for extended periods. The new business becomes the vehicle for outsourcing those capabilities to the main corporate.
- To extract additional value from current resources – build a new enterprise around corporate knowledge, capabilities, or other resources that have significance in product market arenas not presently being performed by the firm.
- To introduce competitive force onto internal suppliers – building a new firm that evolves an alternative supplier to current internal supply bases.
- To elaborate on the risk and cost of product development – creating a new business whose target market promises to be bigger than that for which the core product to be offered by the business was originally developed.
- To eliminate non-core activities – building a new business to pursue business opportunities that the firm is in a favorable position to exploit and to eliminate the activities that have no strategic interest.
Youth Entrepreneurship Advantages – Click here
Strategic Entrepreneurship in Corporate Entrepreneurship

Strategic entrepreneurship includes a second main category of approaches to corporate entrepreneurship. While corporate venturing applies company involvement in the creation of new businesses, strategic entrepreneurship corresponds to a wider array of entrepreneurial initiatives, which do not necessarily implicate new businesses being added to the company.
Strategic entrepreneurship applies concurrent opportunity and advantage-pursuing behaviors. The innovations that are the focal attributes of strategic entrepreneurship initiatives characterize the means through which opportunity is capitalized upon. These are innovations that can occur anywhere in the company. By highlighting an opportunity-driven attitude, management pursues to reach and sustain a competitively advantageous status for the firm.
These innovations can define basic transitions from the firms’ past strategies, products, markets, organization structures, processes, capabilities, or business models. Or, these innovations can define basic bases on which the firm is fundamentally differentiated from its industry rivals.
Therefore, two potential concern points can be considered when a firm demonstrates strategic entrepreneurship. those are,
Green Entrepreneurship – Click here
Requirements for Strategic Entrepreneurship
- How much the firm is converting itself compared to where it was before (ex., transforming its products, markets, inner processes, etc.)
- How much the firm is converting itself compared to industry conventions or standards (in terms of product offerings, market definitions, internal processes, and so forth)
Types of Strategic Entrepreneurship
we can identify five forms of strategic entrepreneurship. Those are
- Strategic Renewal
- Sustained Regeneration
- Domain Redefinition
- Organizational Rejuvenation
- Business Model Reconstruction
Let’s discuss each strategic entrepreneurship one by one.
Strategic Renewal
Strategic renewal is the first form of corporate entrepreneurship in which the firm seeks to redefine its association with its markets or industry competitors by fundamentally modifying how it competes, with a focus on the firm’s strategy. Not all firms are pursuing strategic renewal when they opt for a new strategy. It is considered strategic renewal when they represent fundamental repositioning efforts by the firm within its competitive space or new ventures that are established on unique value propositions that vary from accepted industry strategic formulae.
Sustained Regeneration
Sustained regeneration is noticed as the most famous and typical form. It is the method where organizations regularly and continually introduce new products and services or enter new markets the firm is in a constant hunt for entrepreneurial opportunities. Unlike the other forms, sustained regeneration cannot be explained by a single sort of event. It is a continuous process of introducing new products and services or entering a new market. Therefore, it will usually result in incremental innovation and sometimes result in renewed business creation. Firms engaging in sustained regeneration as innovative organizations include cultures, systems, structures, and competencies which help innovation. They conclude that these firms often occur to be learning organizations.
Organizational learning is the process of enhancing activities through adequate knowledge and understanding. So, it is about creating knowledge and utilizing this to enhance or create new products or business processes. Learning is necessary for important change and innovation because it encourages people to deploy new opportunities and develop new options without becoming frozen in a rigid environment that disables improvements. The acquired knowledge through organizational learning must be shared properly throughout the organization to enable the innovation process without deteriorating the knowledge.
Difference between Businessman and Entrepreneur – Click here
Domain Redefinition
Domain redefinition refers to the entrepreneurial sensation whereby the organization proactively builds a new product-market arena that others have not identified or actively sought to manipulate. Firms redefining their field are visionary and they contend in powerful entrepreneurial orientation. Through field, redefinition firms go into a market where there are no competitors in the short run, this defines as the Blue Oceans Strategy. With this first mover, status firms try to accomplish a sustainable competitive advantage when competitors follow.
Blue oceans denote industries that do not identify yet. the unknown market space that is not yet realized by and touched upon by the competition, where the demand is created by the firm instead of competed for. Out of the five forms, domain redefinition is the superior form in which it necessarily results in new business creation.
Technopreneurs Characteristics – Click here
Organizational Rejuvenation
Organizational rejuvenation is the procedure whereby the organization attempts to maintain or enhance its competitive standing by modifying its internal processes, structures, and/or capabilities, where the purpose is to enhance the implementation of the firm’s strategy. Organizational rejuvenation can entail redesigning the organization in a fundamental way, a single innovation that has a prominent impact on the firm, or considerably smaller innovations that collectively contribute to significantly increased organizational efficiency or significance at strategy implementation.
Meaning that the effort in organizational rejuvenation has to have a significant impact on the way the firm’s strategy is executed through internal processes, structures, and/or capabilities. When organizations engage in corporate entrepreneurship, they introduce innovations that transform primary aspects of how the operation is taken out, create value for the buyers, and sustain or enhance the way the organization executes its strategy.
Business Model Reconstruction
Business model reconstruction entails planning or redesigning the core business model or models to enhance operational efficiencies or otherwise distinguish itself from industry competition in ways appreciated by the market.
Business models are the stories that describe how businesses function. These stories address four primary questions. Who is the customer? What does the customer value? How do we earn money in this business? Finally, what is the underlying economic reason that explains how we can offer value to customers at a reasonable cost?
Businesses may be established based on novel business models or they may embrace new business models in their pursuit of competitive advantage. Typical activities within business model reconstruction contain outsourcing (ex: depending on external suppliers for activities previously executed internally to the firm) and, to a smaller extent, vertical integration (ex: bringing elements of the supplier or distributor operations within the ownership or control of the business).
Corporate Partnerships – Read more
Conclusion
No debate, corporate entrepreneurship has been a vital strategic approach to successful contests in today’s global economy. In this article, we discuss the meaning of corporate entrepreneurship and all types of corporate entrepreneurship in today’s world. So, what are your thoughts about corporate entrepreneurship? write it down in our comment section.